4 Key Differentiators to set the Shaw Dome apart

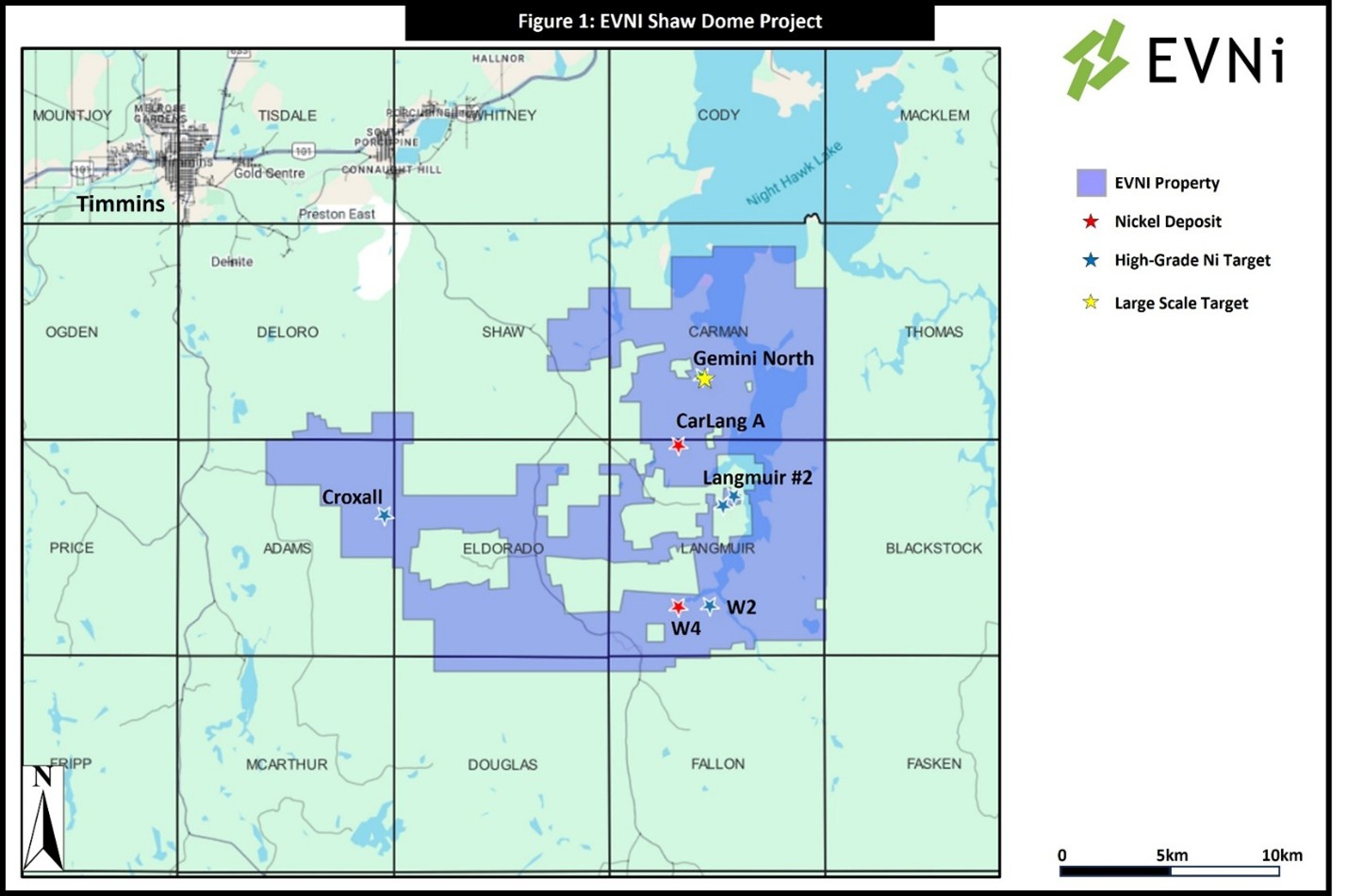
Massive Potential
Our large scale 1B ton resource has extension potential across a 10km strike with a new zone with promising grades and mineralization having been drilled in 2024. The company has a high grade resource, has drilled a second in 2024 and has multiple additional high grade targets. The full package is over 30,000 hectares with more than 100km of strike to explore.
Best Location
Easy access to Timmins – an established mining center with labour and suppliers.
Clean Hydro Power
Grid power to the Project, draws electricity from Northern Ontario hydro.